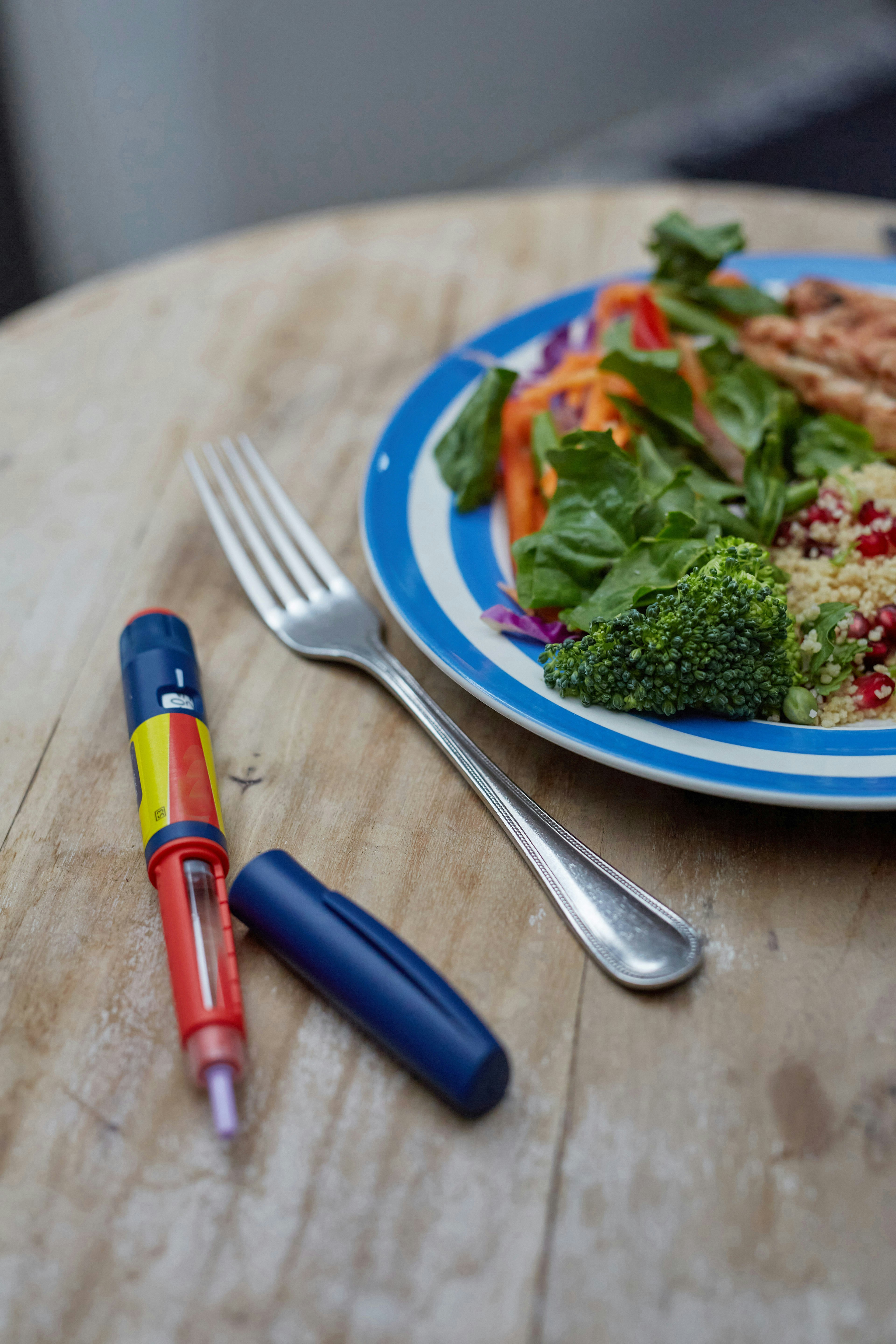Understanding Diabetic Weight Loss
Weight management plays a crucial role in the health and well-being of individuals diagnosed with diabetes, especially for those who are overweight. The connection between body weight and blood sugar levels is significant; excess body fat can lead to insulin resistance, making diabetes more difficult to control. A diabetic weight loss diet is essential for stabilizing blood glucose levels, ultimately reducing the risk of complications associated with this condition, including cardiovascular diseases, neuropathy, and kidney damage.
Implementing an effective weight loss strategy requires a focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods while minimizing processed and high-sugar options. Adopting a balanced diet that emphasizes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables can help individuals not only lose weight but also achieve better diabetes management. The goal is to create a sustainable lifestyle change rather than a temporary diet, leading to lasting results.
Beyond the physical benefits, psychological factors significantly influence weight loss success in diabetic individuals. Many may experience frustration or despair due to the challenges of living with diabetes, which can hinder motivation for weight loss. However, understanding that weight management can lead to improvements in overall health, increased energy levels, and potentially even remission of diabetes can be empowering. Setting realistic weight loss goals and celebrating gradual progress can foster a positive mindset, making it easier to comply with a healthier lifestyle.
Moreover, supportive communities or professional guidance, such as nutritionists or diabetes educators, can play a pivotal role in providing motivation and accountability. By approaching weight loss in a holistic manner, individuals with diabetes may find a path to achieving not only a healthier weight but also improved emotional well-being and a better quality of life.
Key Food Groups for a Diabetic Diet
Adopting a balanced diet is crucial for individuals managing diabetes, particularly when it comes to weight loss. A well-rounded diabetic diet should incorporate essential food groups while emphasizing proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in moderation. Each of these macronutrients plays a significant role in maintaining blood sugar levels and promoting overall health.
Protein sources, such as lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, and low-fat dairy, are vital for muscle maintenance and the feeling of fullness. Including these foods in a diabetic weight loss diet can help stabilize blood glucose levels and reduce cravings. Special attention should be given to omega-3 fatty acids, primarily found in fatty fish and flaxseeds. Research suggests that omega-3s may lower inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity, making them a valuable addition to a diabetic meal plan.
Carbohydrates require careful consideration as they can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, beans, and starchy vegetables, should be prioritized over simple carbohydrates like sugary snacks and white bread. High-fiber foods are also essential, as they slow digestion and promote better glycemic control. Increasing fiber intake can be achieved by incorporating fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds into daily meals.
While fruits are a natural source of vitamins and minerals, they also contain natural sugars that can affect blood sugar levels. It is essential to consume fruits in moderation and opt for low-glycemic options, such as berries and apples, over high-glycemic fruits like bananas and grapes. This approach allows for the inclusion of fruits in the diet without leading to significant spikes in blood sugar.
In summary, creating a diabetic weight loss diet requires a balanced approach, carefully choosing proteins, healthy fats, and carbohydrates while monitoring fruit intake to maintain stable blood sugar levels and overall health.
Meal Planning and Blood Sugar Monitoring
Effective meal planning is a cornerstone for individuals managing diabetes, as it helps maintain blood sugar levels within target ranges. This tailored approach to nutrition not only focuses on the types of foods consumed but also emphasizes portion sizes, meal timings, and dietary balance. A well-structured meal plan should include a variety of foods rich in nutrients, ensuring an intake of proteins, healthy fats, and fiber, all while minimizing added sugars and refined carbohydrates. By incorporating whole grains, legumes, lean proteins, and plenty of vegetables, individuals can create meals that promote satiety and stabilize blood sugar.
Balancing meals is essential, particularly for those with diabetes. One practical method involves using the plate method, where half of the plate is filled with non-starchy vegetables, a quarter with lean protein, and the remaining quarter with healthy carbohydrates. This approach not only simplifies meal preparation but also helps in visualizing appropriate portion sizes. It is important to consider individual needs and preferences; therefore, customizing meals based on personal food choices and tolerances is critical for success in a diabetic weight loss diet.
In addition to meal planning, monitoring blood sugar levels is a vital component of diabetes management. Regularly checking glucose levels before and after meals allows individuals to understand how specific foods affect their body. Keeping a food journal can further aid in this process by providing a detailed account of meals consumed, portion sizes, and subsequent blood sugar readings. By tracking this information, individuals can make more informed decisions about their diet, cooking methods, and ingredient selections, ultimately leading to better control over their diabetes and supporting their weight loss goals.
Resources and Support for a Healthy Lifestyle
Embarking on a diabetic weight loss diet can feel overwhelming, but various resources and support systems are available to guide individuals on their journey toward better health. One of the most reputable organizations dedicated to improving the lives of those with diabetes is the American Diabetes Association (ADA). The ADA provides extensive information on dietary choices, including meal planning, carbohydrate counting, and strategies for integrating physical activity into daily life. Their resources are designed to empower individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions regarding their nutrition and overall lifestyle.
In addition to the ADA, numerous organizations and websites offer valuable insights into diabetic nutrition. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides educational materials that cover everything from understanding diabetes management to learning about healthy eating habits. These resources not only help individuals understand their condition but also encourage them to adopt healthier lifestyles through practical tips and evidence-based recommendations.
Seeking personalized guidance from healthcare professionals, such as registered dietitians and certified diabetes educators, is crucial for tailoring dietary needs to each individual. These experts can assess personal health goals, preferences, and metabolic responses to create a comprehensive meal plan. This personalized approach ensures that the dietary regimen is manageable and sustainable, leading to better adherence and success in achieving weight loss goals.
Furthermore, surrounding oneself with a supportive community can significantly enhance the weight loss journey. Joining local or online diabetes support groups can provide encouragement, shared experiences, and motivation. Engaging with others facing similar challenges fosters a sense of belonging, making it easier to maintain dietary commitments. In conclusion, leveraging these resources and professional support can cultivate a healthier lifestyle, benefiting both physical and emotional well-being.
Published by May Healthy Lifestyle